10 Key Business Process Automation Examples for 2025
Discuss with AI
Get instant insights and ask questions about this topic with AI assistants.
💡 Pro tip: All options include context about this blog post. Feel free to modify the prompt to ask more specific questions!
Business process automation (BPA) is more than just a popular term; it's a fundamental shift in how modern companies operate, compete, and scale. By strategically applying technology to handle repetitive, rule-based tasks, businesses can unlock significant gains in efficiency, reduce costly human errors, and free up valuable team members to focus on high-impact strategic work. This isn't about replacing people; it's about empowering them with smarter tools to achieve better results.
This guide moves beyond generic definitions to provide a comprehensive list of actionable business process automation examples. We will break down specific use cases across critical departments, including marketing, customer support, finance, and operations. You will learn not just what to automate, but how to implement these systems effectively and what strategic benefits to expect.
Each example is designed to serve as a practical blueprint. We will dissect the process, highlight key tactics, and provide clear takeaways you can apply directly to your own workflows. Whether you manage an e-commerce store, lead a customer support team, or oversee marketing campaigns, this article will equip you with replicable strategies to streamline operations. Prepare to explore tangible business process automation examples that demonstrate how platforms like Spur can transform your core processes, from initial customer contact to final financial reporting. You will see firsthand how automation drives measurable growth and enhances operational resilience.
At its core, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) automation uses software to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. It’s one of the most foundational business process automation examples, aiming to improve business relationships with customers, assist in customer retention, and drive sales growth. By automating routine sales, marketing, and customer service tasks, teams can focus on strategic, high-value activities instead of manual data entry and repetitive communication.
For example, a system like HubSpot can automatically enroll a new website lead into a targeted email nurturing sequence based on the content they downloaded. Similarly, Salesforce can instantly assign that lead to the correct sales representative based on predefined rules like geographic territory or company size, ensuring rapid follow-up. This level of automation creates a seamless, personalized customer journey from the very first interaction.
The primary goal of CRM automation is to create operational efficiency and a unified customer view. By connecting data from various touchpoints such as email, social media, and your website, you build a comprehensive profile for every contact. This allows for hyper-personalized marketing and sales efforts at scale.
Key Insight: Effective CRM automation isn't just about sending automated emails. It’s about creating intelligent workflows that respond to customer behavior in real-time, delivering the right message at the right moment to guide them through the sales funnel.
This bar chart illustrates the direct financial benefits reported by businesses that implement CRM automation.
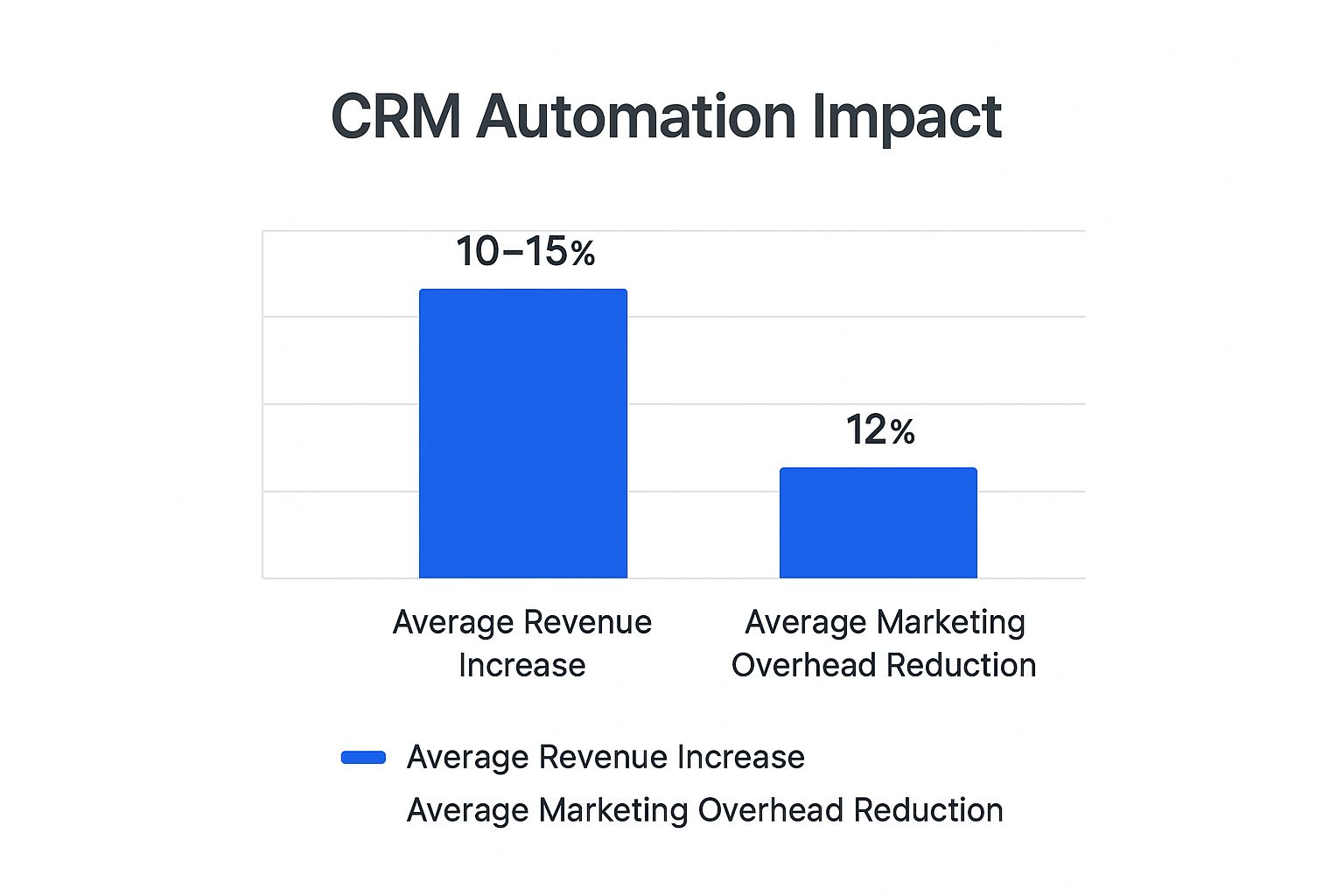
The data clearly shows that automation not only boosts top-line revenue but also significantly cuts operational costs.
To successfully implement CRM automation, follow these best practices:
- Start Simple: Begin by automating a single, high-impact process, such as lead assignment or welcome email sequences.
- Prioritize Data Quality: Establish and enforce clear data entry standards for your team to ensure your automation workflows run on accurate information.
- Integrate Key Channels: To maximize impact, consider integrating popular communication channels directly into your system. For instance, you can integrate WhatsApp with your CRM to capture conversations and automate follow-ups.
- Train and Optimize: Regularly train your team on using the system and review your automated workflows quarterly to identify areas for improvement.
Accounts Payable (AP) and invoice processing automation uses technology to digitize and streamline the entire invoice management lifecycle, from receipt to final payment. This powerful business process automation example leverages tools like Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and machine learning to capture invoice data, validate it, route it for approval, and execute payment. The goal is to eliminate manual data entry, reduce human error, and accelerate payment cycles, freeing up finance teams to focus on more strategic financial analysis.

For instance, a global enterprise like Siemens successfully used AP automation to reduce its invoice processing time from an average of 12 days down to just 4. Similarly, Walmart manages a massive volume of over one million invoices monthly through a highly automated system. These systems automatically match invoices to purchase orders and receipts, flag exceptions, and schedule payments, ensuring accuracy and compliance on an enormous scale.
The core objective of AP automation is to transform a traditionally slow, paper-heavy, and error-prone function into a fast, digital, and highly efficient operation. By automating tasks like data extraction and three-way matching, businesses dramatically reduce processing costs and minimize the risk of late payment fees or duplicate payments. This provides real-time visibility into liabilities and cash flow, which is critical for accurate financial forecasting and strategic decision-making.
Key Insight: True AP automation extends beyond simple data entry. It’s about creating an intelligent, end-to-end workflow that enforces financial controls, maintains a clear audit trail, and provides valuable data analytics on spending patterns and vendor performance.
This strategic shift turns the AP department from a cost center into a source of valuable business intelligence.
To effectively implement AP and invoice processing automation, consider these best practices:
- Standardize Inputs: Work with your key vendors to standardize invoice formats where possible. This simplifies data extraction and reduces exceptions.
- Define Clear Hierarchies: Before going live, establish and configure clear approval workflows and spending limits within the system to maintain financial governance.
- Implement in Phases: Start by automating processes for high-volume, low-complexity vendors. A gradual rollout allows your team to adapt and helps you refine the system before expanding it company-wide.
- Maintain Manual Overrides: Ensure your system includes a robust exception-handling process. This allows your team to manually intervene and resolve complex or unusual invoices without disrupting the entire automated flow.
Human Resources onboarding automation streamlines the process of integrating new employees into a company. It uses technology to manage everything from initial paperwork and document collection to IT system provisioning, training module assignments, and scheduled check-ins. This is a critical business process automation example because it ensures every new hire receives a consistent, comprehensive, and welcoming experience, freeing the HR team from repetitive administrative tasks.
For example, platforms like Workday or BambooHR can automatically trigger a series of actions once a candidate accepts a job offer. This includes sending out digital contract and tax forms for e-signature, creating user accounts in essential systems like Slack and email, and enrolling the new hire in mandatory first-week training courses. Shopify successfully automated over 80% of its onboarding tasks, creating a scalable process that supports its rapid growth.
The core strategic goal of onboarding automation is to improve new hire retention and accelerate their time-to-productivity. A chaotic or slow onboarding process can lead to early disengagement and turnover, whereas a smooth, automated workflow makes employees feel valued and prepared from day one. It standardizes the experience, ensuring no crucial steps are missed, regardless of the hiring manager or department.
Key Insight: Effective onboarding automation is not about removing human interaction; it's about automating the administrative burden so HR and team leads can focus on high-value, human-centric activities like mentorship, team integration, and cultural immersion.
This strategic shift turns onboarding from a logistical hurdle into a powerful tool for building company culture and employee loyalty. For a deeper dive into streamlining human resources, explore how HR process automation can transform your entire workplace.
To effectively implement HR onboarding automation, consider these best practices:
- Map the Journey: Before automating anything, thoroughly map out the entire employee onboarding journey from offer acceptance to the 90-day review.
- Create Role-Specific Templates: Develop different automated onboarding workflows for different roles or departments to ensure the information and access provided are relevant.
- Maintain the Human Touch: Schedule automated reminders for managers to conduct personal check-ins and plan team welcome lunches.
- Gather Feedback: Use automated surveys to collect feedback from new hires about their onboarding experience, and use that data to continuously refine and improve the process.
Email marketing automation uses software to send personalized, timely messages to subscribers based on specific triggers, behaviors, and data points. It is a cornerstone among business process automation examples, allowing companies to nurture leads, engage customers, and drive sales without manual intervention for every send. By creating automated workflows, businesses can deliver highly relevant content that moves subscribers through the customer journey efficiently.
For instance, e-commerce platform Klaviyo can automatically send a "browse abandonment" email to a shopper who viewed a specific product but didn't add it to their cart. Similarly, Spotify uses automation to send its famous "Wrapped" year-in-review summaries and weekly "Discover Weekly" playlists, creating a personalized experience that keeps users engaged with the platform. These automated systems work 24/7 to capitalize on user interest at the perfect moment.
The core strategy behind email marketing automation is to scale personalization and timeliness. Instead of blasting one generic message to an entire list, automation allows you to segment your audience and trigger communications based on actions like a purchase, a website visit, or a period of inactivity. This creates a dynamic, one-to-one conversation that builds stronger customer relationships and increases conversion rates.
Key Insight: Advanced email automation transcends simple triggers. It's about building a behavioral ecosystem where each customer action informs the next communication, creating a predictive and responsive marketing engine that anticipates customer needs.
This targeted approach ensures that your marketing efforts are not just seen as noise but as a valuable service, delivering relevant information precisely when it's most useful to the recipient.
To effectively implement email marketing automation, follow these best practices:
- Start with Foundational Flows: Begin by building essential automated series, such as a welcome sequence for new subscribers or an abandoned cart reminder for e-commerce.
- Segment Beyond Demographics: Create dynamic segments based on user behavior, like purchase history, engagement level, and website activity, for more relevant messaging.
- A/B Test Everything: Continuously test elements like subject lines, send times, and content within your automated flows to optimize for higher open rates and conversions.
- Prioritize a Clean List: Regularly clean your email list to remove inactive subscribers. This improves deliverability, reduces costs, and ensures your workflows are targeting an engaged audience.
IT Help Desk and Ticketing Automation streamlines internal support processes by using software to manage, categorize, prioritize, and route employee support requests. This is a crucial business process automation example for maintaining operational continuity and productivity. By automating repetitive tasks like ticket assignment, password resets, and initial diagnostics, the IT team is freed from low-level issues to concentrate on complex, strategic infrastructure projects.
For instance, a platform like Jira Service Management can automatically route a "new software request" ticket to the procurement department, while a "VPN access issue" ticket is sent directly to the network security team. Similarly, many enterprises leverage ServiceNow to automate up to 70% of their routine IT requests, using self-service portals and chatbots to resolve common problems like printer setup or software installation without any human intervention. This automation ensures issues are addressed faster and by the right people, minimizing employee downtime.
The core strategic objective of IT automation is to reduce Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) and improve the employee service experience. By creating predefined workflows for common issues, businesses can deliver consistent and rapid solutions. It also builds a valuable data repository of IT problems, which can be analyzed to identify recurring issues, faulty equipment, or areas needing better user training.
Key Insight: The most advanced IT automation moves beyond simple routing. It involves creating a comprehensive knowledge base that powers self-service portals and chatbots, empowering employees to find answers instantly and deflecting a significant percentage of tickets from ever reaching the help desk.
This approach not only cuts support costs but also fosters a more self-sufficient and tech-literate workforce.
To effectively implement IT help desk automation, follow these best practices:
- Start with High-Volume Requests: Begin by identifying and automating the most common and repetitive tickets, such as password resets or access requests, to achieve the quickest impact.
- Invest in a Knowledge Base: Develop a comprehensive and easy-to-search knowledge base. This is the foundation for successful self-service portals and automated chatbot responses.
- Define Escalation Paths: Create clear, automated escalation rules. If a chatbot cannot resolve an issue after two attempts, the ticket should be automatically routed to a Level 1 human agent.
- Analyze Ticket Data: Regularly review ticket data to spot trends. For more guidance, discover the best practices for help desk management to identify new opportunities for automation and process improvement.
Supply chain automation leverages technology to optimize the end-to-end flow of goods, from procurement and manufacturing to inventory management and final delivery. This is a critical area of business process automation, as it directly impacts costs, customer satisfaction, and operational resilience. By automating routine tasks like inventory tracking, order processing, and supplier communication, companies can minimize human error, reduce overhead, and respond more quickly to market changes.

For instance, a system like Oracle SCM can use predictive analytics to forecast demand and automatically generate purchase orders when stock levels hit a predetermined threshold. This prevents stockouts and overstocking. Similarly, Amazon's fulfillment centers use a combination of robotics and sophisticated software to pick, pack, and ship millions of orders with incredible speed and accuracy, showcasing automation at a massive scale.
The core strategic goal of supply chain automation is to create a transparent, agile, and cost-effective logistics network. It connects disparate systems, including suppliers, warehouses, and shipping carriers, into a single, cohesive ecosystem. This unified view enables businesses to make data-driven decisions, anticipate disruptions, and optimize inventory levels across all locations.
Key Insight: Advanced supply chain automation moves beyond simple reordering. It's about creating a self-regulating system that uses real-time data to dynamically adjust to demand fluctuations, shipping delays, and supplier performance, ensuring operational continuity.
This video provides a deeper look into how modern automation is transforming supply chain logistics.
To effectively implement supply chain automation, consider these best practices:
- Start with Predictable Items: Begin by automating the inventory management for your high-volume, predictable products to build a solid foundation and prove ROI.
- Establish Data Governance: Ensure your product, supplier, and inventory data is clean and standardized. Automation is only as good as the data it runs on.
- Integrate Warehouse Operations: For businesses looking to optimize their physical operations, exploring the capabilities of warehouse automation software can significantly enhance efficiency from receiving to shipping.
- Collaborate with Partners: Work closely with your key suppliers and logistics partners to integrate systems. Shared data visibility is crucial for a truly automated supply chain.
Financial Reporting and Reconciliation Automation involves using software to streamline critical accounting tasks like month-end closes, account reconciliations, and regulatory reporting. This is one of the most impactful business process automation examples for finance departments, as it eliminates error-prone manual data consolidation and spreadsheet management. By automatically pulling data from various sources like bank accounts, ERPs, and payment gateways, these systems perform calculations and generate standardized reports with built-in controls and audit trails.
For example, a solution like BlackLine can automate up to 90% of a company’s routine reconciliation processes, allowing accountants to focus only on exceptions. Similarly, global enterprises like Unilever have implemented financial automation across 190 countries to standardize processes and drastically reduce their month-end close time. This automation ensures accuracy, enhances compliance, and frees up finance professionals for more strategic analysis.
The core purpose of automating financial reporting is to increase speed, accuracy, and compliance while reducing operational costs. By standardizing the chart of accounts and workflows before implementation, businesses can create a “single source of truth” for financial data. This unified view is essential for reliable forecasting, budgeting, and making agile business decisions.
Key Insight: True financial automation extends beyond simple task completion. It’s about creating a transparent, auditable, and resilient financial ecosystem where data integrity is maintained automatically, giving leaders high-confidence numbers to drive strategy.
This automation transforms the finance function from a reactive, historical record-keeper into a proactive, strategic business partner.
To effectively implement financial reporting automation, adhere to these best practices:
- Standardize First: Before automating, standardize your chart of accounts and define clear, consistent processes for all financial tasks.
- Implement Data Validation: Build robust data quality checks into your automated workflows to catch and flag inconsistencies before they enter your reports.
- Maintain Manual Overrides: Ensure your system allows for manual intervention. This is crucial for handling complex, non-standard transactions that require human judgment.
- Regularly Audit Controls: Periodically review and update your automated controls to ensure they remain aligned with current accounting standards and regulatory compliance requirements.
Social media automation involves using software to manage and execute tasks across various platforms, such as scheduling posts, monitoring conversations, and analyzing performance. This is one of the most visible business process automation examples, allowing brands to maintain a consistent online presence and engage with their audience at scale. It frees up social media managers from repetitive tasks like manual posting, letting them focus on strategy, content creation, and genuine community interaction.
For instance, a tool like Buffer or Later can schedule a week's worth of content across Instagram, X (formerly Twitter), and Facebook, automatically publishing posts at times optimized for maximum engagement. Similarly, a platform like Sprout Social can monitor brand mentions and keywords in real-time, allowing a community manager to quickly respond to customer service inquiries or jump into relevant conversations, creating a proactive and responsive brand image.
The core strategic purpose of social media automation is to achieve brand consistency and operational scalability. By planning and scheduling content in advance, businesses ensure a steady stream of communication, reinforcing brand messaging and keeping their audience engaged. This automation also enables a more data-driven approach, using analytics to refine content strategy, posting frequency, and platform focus.
Key Insight: True social media automation extends beyond just scheduling posts. It's about creating an integrated system that listens to audience signals, automates appropriate responses, and funnels critical conversations to human agents for authentic engagement, blending efficiency with a personal touch.
This systematic approach ensures that no opportunity for engagement is missed, while also providing valuable data on what resonates with your audience.
To effectively leverage social media automation, consider these best practices:
- Balance Automation and Authenticity: Schedule foundational content but leave room for spontaneous, real-time posts that reflect current events or trending topics.
- Establish Escalation Protocols: Create clear guidelines for your team on which comments or messages (e.g., sensitive complaints) require immediate human intervention.
- Customize Content for Each Platform: Avoid simply cross-posting the exact same message. Tailor the copy, image format, and hashtags for the unique audience and algorithm of each platform.
- Monitor Brand Sentiment: Use automation tools to continuously track brand mentions and sentiment, allowing you to protect your brand's reputation proactively. You can explore a variety of social media automation tools to find the one that best fits your monitoring and scheduling needs.
Data backup and disaster recovery automation involves using specialized software to ensure business continuity by automatically creating, managing, and testing data backups. This form of automation provides rapid recovery capabilities in the event of data loss, system failure, or a cyber-attack. It moves beyond simple scheduled backups by automating the entire lifecycle, from data capture to recovery verification, minimizing the risk of human error and significantly reducing downtime.
For instance, major cloud providers like AWS and Microsoft Azure offer automated backup services that can take snapshots of entire servers and databases at predefined intervals. A company like Dropbox demonstrates this at a massive scale, automatically replicating user data across multiple global data centers. This ensures that even if one center goes offline, user files remain accessible and secure, a critical function for maintaining trust and service availability.
The strategic goal of this automation is to build a resilient operational infrastructure that can withstand unforeseen events. By automating the backup process, organizations ensure that data is consistently protected without requiring constant manual oversight. This frees up IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than performing tedious, repetitive backup tasks, which are often prone to being forgotten or done incorrectly.
Key Insight: True disaster recovery automation isn't just about making copies of data; it's about automating the validation and recovery processes. The ability to automatically test backups and execute a recovery plan ensures your business can get back online in minutes, not days.
Automating these processes is a core component of modern risk management and a powerful example of business process automation that safeguards a company’s most valuable asset: its data.
To effectively implement backup and disaster recovery automation, consider these best practices:
- Implement the 3-2-1 Rule: Automate a workflow that creates three copies of your data, on two different types of media, with one copy stored off-site.
- Test Recovery, Not Just Backups: Schedule automated, non-disruptive recovery tests in a sandboxed environment to regularly verify that your backups are viable and your recovery plan works as expected.
- Automate Monitoring and Alerts: Set up automated alerts to notify your team of backup failures, successes, or data integrity issues. This ensures immediate awareness and action.
- Document and Rehearse: While the process is automated, the plan must be documented. Use automation to trigger regular reviews and simulated disaster drills with your team.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Testing Automation involves using specialized software to execute pre-scripted tests on a software application before it is released to the public. This process is a cornerstone of modern software development, automating repetitive but critical tasks like functional, regression, and performance testing. By integrating these automated tests into the development pipeline, companies can ensure consistent quality, accelerate release cycles, and free up human testers to focus on more complex, exploratory testing scenarios.
For instance, a tool like Selenium or Cypress can automatically run a suite of tests that simulate a user navigating an e-commerce website, adding items to their cart, and completing a checkout. This ensures core functionality isn't broken after a new code update. Similarly, tools like Jenkins can trigger these tests automatically every time a developer commits new code, providing immediate feedback on quality and preventing bugs from reaching production.
The core strategic value of QA automation is its ability to provide a rapid, reliable feedback loop within the software development lifecycle (SDLC). It shifts quality control from a final-stage bottleneck to a continuous, integrated process. This "shift-left" approach catches bugs earlier when they are cheaper and easier to fix, directly reducing development costs and improving product stability.
Key Insight: Effective QA automation is not about replacing manual testers but empowering them. It handles the high-volume, predictable checks, allowing QA professionals to apply their critical thinking to edge cases, user experience, and complex system interactions that automation cannot easily cover.
This strategy enables a culture of continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), allowing tech giants like Spotify and Google to deploy new features multiple times a day with confidence.
To effectively implement QA automation, consider these best practices:
- Start with Stable, High-Value Tests: Begin by automating test cases for the most critical and stable parts of your application, such as user login or checkout processes, to maximize immediate ROI.
- Integrate into the Development Process: Use CI/CD tools like Jenkins or CircleCI to make automated testing an integral part of your development workflow, not a separate, after-the-fact step.
- Balance Automated and Manual Testing: Acknowledge that not everything can or should be automated. Maintain a healthy balance, using automation for regression and performance tests while reserving manual testing for usability and exploratory analysis.
- Invest in Maintainable Frameworks: Choose a scalable and maintainable test framework. Document your tests and follow coding best practices to ensure your automation suite remains a valuable asset, not a technical debt burden.
Automation Type Implementation Complexity 🔄 Resource Requirements ⚡ Expected Outcomes 📊 Ideal Use Cases 💡 Key Advantages ⭐ Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Automation High: setup, customization, training Moderate to high: software, staff training 10-15% revenue increase, 12% marketing overhead reduction Sales & marketing process automation Improved lead conversion, personalized interactions Accounts Payable and Invoice Processing Automation Medium to high: OCR, workflow config Moderate: software, vendor coordination 70-90% reduction in processing time, ROI in 6-12 months Invoice processing and payment workflows Faster payments, error reduction, better cash flow Human Resources Onboarding Automation Medium: configuration and integration Moderate: HRIS, IT, training resources 18% higher revenue growth, 25% improved retention New employee onboarding Faster productivity, consistent onboarding, compliance Email Marketing Automation Medium: setup of workflows and content Moderate: marketing team, platform tools 320% more revenue, 70.5% higher open rates Customer engagement and retention Personalized messaging, scalable campaigns IT Help Desk and Ticketing Automation Medium to high: process mapping, integration Moderate: IT staff, knowledge base upkeep 30-50% faster resolution, 25-40% better first-call fix IT support and service desk Faster response, resource optimization Supply Chain and Inventory Management Automation High: integration, forecasting complexity High: ERP, suppliers, analytics platforms 15-25% inventory cost savings, 20-30% faster order processing Procurement, inventory control, logistics Reduced stockouts, cost savings, improved supplier relations Financial Reporting and Reconciliation Automation High: process standardization, integration High: financial systems, skilled personnel 30-50% faster closes, 85-95% accuracy Month-end closing, compliance reporting Accuracy, compliance, faster reporting Social Media Management and Content Automation Medium: content strategy and platform setup Moderate: marketing resources, AI tools 23% engagement increase, 18% faster responses Brand presence and social engagement Consistency, time savings, scalable operations Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Automation High: infrastructure and system complexity High: storage, bandwidth, cloud services 70-80% fewer data loss incidents, recovery time in minutes Data protection and business continuity Guaranteed backups, rapid recovery Quality Assurance and Testing Automation High: tool setup, script maintenance High: skilled testers, development support 40-70% reduction in testing time, 25-45% fewer defects Software testing and deployment cycles Increased quality, faster releases
We've journeyed through a comprehensive landscape of business process automation examples, from streamlining your accounts payable and financial reporting to revolutionizing customer support and social media management. Each use case, whether it's automating HR onboarding or fortifying your data backup protocols, illustrates a powerful, unifying theme: automation is no longer a luxury for large enterprises. It's an accessible, strategic imperative for businesses of all sizes, especially in the competitive e-commerce and D2C spaces.
The core takeaway is that effective automation isn't about replacing human ingenuity; it's about augmenting it. By delegating repetitive, rule-based tasks to intelligent systems, you liberate your team to focus on high-value activities that demand creativity, strategic thinking, and genuine human connection. This shift is the fundamental driver of both efficiency and innovation.
Reflecting on the diverse business process automation examples covered, several strategic principles emerge:
- Start with Pain Points: The most successful automation initiatives begin by identifying the biggest bottlenecks, most error-prone processes, or most time-consuming tasks within your organization. Don't automate for the sake of technology; automate to solve a real, measurable problem.
- Interdepartmental Impact: Notice how automating one area, like inventory management, has a ripple effect on sales, customer support, and finance. True optimization happens when you view your business as an interconnected ecosystem, not a collection of isolated silos.
- Data is the Fuel: Every automation workflow, from personalized email marketing to IT help desk ticketing, runs on data. The quality, accessibility, and integration of your data will directly determine the success and intelligence of your automated processes.
- Scalability is a Prerequisite: The solutions you implement today must be able to grow with you. An automation platform that handles 100 invoices a month should be just as capable of handling 10,000 without requiring a complete overhaul.
Moving from theory to practice can feel daunting, but it’s a journey of a thousand small, strategic steps. Here’s how you can begin implementing what you’ve learned from these examples today.
- Conduct an Automation Audit: Gather your team leaders from marketing, sales, support, and operations. Dedicate a meeting to mapping out your key processes. Use a simple framework for each process:
- What is the task?
- How much time does it take weekly?
- Is it rule-based and repetitive?
- What is the business impact of automating it?
- Prioritize for High-Impact, Low-Effort Wins: From your audit, identify the "low-hanging fruit." These are typically tasks that are highly repetitive but relatively simple to automate. Early wins, like setting up automated email responses for common support queries or an automated social media posting schedule, build momentum and demonstrate immediate value.
- Select the Right Tools for the Job: Your technology stack is crucial. You need a platform that is both powerful and user-friendly, capable of integrating with the tools you already use (like your CRM, e-commerce platform, and help desk software). Flexibility is key. For a broader overview and additional ideas, explore these top business process automation examples that can significantly boost efficiency.
Strategic Note: The goal is not to find a single tool that does everything, but to build a cohesive ecosystem of tools that communicate seamlessly. Look for platforms with robust API capabilities and pre-built integrations to make this process smoother.
Embracing the strategies outlined in these business process automation examples is a commitment to building a more resilient, efficient, and intelligent business. It’s about creating an operational framework that empowers your team, delights your customers, and positions your company for sustainable growth in an increasingly digital world. The journey starts not with a massive technological overhaul, but with a single, well-chosen process.
Ready to turn these examples into your reality? Spur empowers you to build the AI-powered workflows your business needs without writing a single line of code. Connect your favorite apps, automate complex processes, and unlock new levels of efficiency with our intuitive, powerful platform. Start building your automated future with Spur today.
